If you’re studying IFRS 7 Financial Instruments – Disclosures, here’s a short one page summary we’ve just launched. You can buy these summaries as part of a pack, by clicking here.
Update: IAS 33 Earnings per Share quiz
IAS 33 Earnings per Share can be a tricky topic to grasp. You might find it easier to study IAS 33 using one of our quizzes.
Update: IAS 36 Impairment of Assets quiz
Students who practice questions generally learn more effectively than those who don’t. If you’re studying IAS 36 Impairment, why not test your knowledge with our multiple choice quiz?
The 4 Step Acqusition Method for Business Combinations under IFRS 3
Under IFRS 3, a business combination must be accounted for using a technique called the “acquisition method”. This views the transaction from the perspective of the acquirer and involves the following stages:
- Identify acquirer
- Determine acquisition date
- Recognise and measure
Assets, liabilities and NCI in acquiree
at FV at the acquisition date - Goodwill/Bargain purchase
Difference between consideration paid and net assets acquired
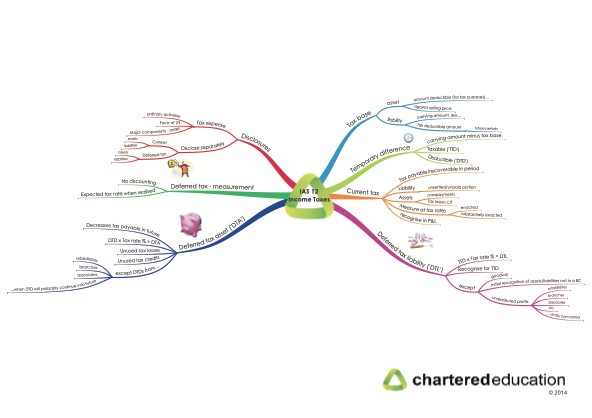
New mind map: IAS 12 Income Taxes
A request was recently received for a mind map on IAS 12 Income Taxes, so here you go! I hope it’s useful to you.
How do you calculate goodwill? Your 30 second recap for IFRS 3
When an acquirer doesn’t own all the shares in an acquiree, the equity in the subsidiary not held by the acquiree is called the non-controlling interest (‘NCI’)
NCI resulting from a business combination is measured at:
- The NCI’s proportionate share of the acquiree’s identifiable net assets (partial goodwill method), or
- Fair value (full goodwill method)
Update: IAS 16 Property Plant and Equipment quiz
If you’re studying IAS 16 Property, Plant and Equipment, why not test your knowledge with our multiple choice quiz? Click here to test yourself. By practicing questions, you’ll improve your study and recall, ideal for people who learn best by ‘doing’ rather than just reading.
Fundamental Characteristics of the IASB Conceptual Framework
You might remember the fundamental characteristics of useful financial information (per the IASB Conceptual Framework) are:
- Relevance, and
- Faithful Representation
New mind map and summary note: IFRS 13 Fair Value Measurement
A student recently requested a summary note and mind map for IFRS13 Fair Value Measurement. All the IFRS mind maps and summary notes are available from our IFRS store.
Two Types of Government Grant for under IAS 20
As you may know, there are two types of grants; revenue based grants (Grants relating to income) and capital grants (Grants related to assets).
In your career, you’ll need to be able to apply the provisions of relevant accounting standards in relation to accounting for government grants. IAS 20 Accounting for Government Grants and Disclosure of Government Assistance is the IFRS applicable to government grants.